what is the banker's algorithm
The Bankers algorithm was developed by Edsger Dijkstra, which is a resource allocation and deadlock avoidance algorithm. Banker's algorithm is designed to check the Safe / Unsafe state of requested resources.
The data structure of the Bankers algorithm mainly does have four components AVAILABLE, MAX, ALLOCATION, and NEED.
| n | A total number of processes. |
| m | A total number of resource types. |
| Available | A length of vector m. Which shows a number of available resources of each type. If Available[i] = k, then k instances of resource Ri are available. |
| Max | An n×m matrix that contains maximum demand for each process. If Max[i,j] = k, then process Pi can request maximum k instances of resource type Rj. |
| Allocation | An n×m matrix that contains a number of resources of each type currently allocated to each process. If Allocation[i,j] = k, then Pi is currently allocated k instances of resource type Rj. |
| Need | An n×m matrix that shows the remaining resource need of each process. If Need[i,j] = k, then process Pi may need k more instances of resource type Rj to complete the task. |
Bankers algorithm example statements:
Reena’s operating system uses an algorithm for deadlock avoidance to manage the allocation of resources say three namely A, B, and C to three processes P0, P1, and P2.
Consider the following scenario as reference .user must enter the current state of the system as given in this example: Suppose P0 has 0,0,1 instances, P1 is having 3,2,0 instances and P2 occupies 2,1,1 instances of A, B, C resource respectively.
Also, the maximum number of instances required for P0 is 8,4,3 and for p1 is 6,2,0 and finally, for P2 there are 3,3,3 instances of resources A, B, C respectively. There are 3 instances of resource A, 2 instances of resource B and 2 instances of resource C available.
Write a program to check whether Reena’s operating system is in a safe state or not in the following independent requests for additional resources in the current state: 1. Request1: P0 requests 0 instances of A and 0 instances of B and 2 instances of C. 2. Request 2: P1 requests for 2 instances of A, 0 instances of B and 0 instances of C. All the requests must be given by the user as input.
As per the above problem statement, Below is the initial safe state.
| Process | Max | Allocation | Need | ||||||
| A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| P0 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||
| P1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | |||
| P2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| AVAILABLE | X=3, Y=2, Z=2 | ||||
On initial state, If Request 1 is permitted P0=0, P1=0, P2=2 then the state would become,
| Process | Max | Allocation | Need | ||||||
| A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| P0 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 0 |
| P1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| P2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| AVAILABLE | X=3, Y=2, Z=0 | ||||
Now, With the above-mentioned Availability, we can service the process P1. After that, the next state would become
| Process | Max | Allocation | Need | ||||||
| A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| P0 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8 | 4 | 0 |
| P1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| AVAILABLE | X=6, Y=4, Z=0 | ||||
Considering the above availability, It would not possible to provide instances to process P0 and P1. Hence, the system would go into a deadlock state. So, we can not permit request 1.
On initial state, If Request 1 is permitted P0=2, P1=0, P2=0 then the state would become,
| Process | Max | Allocation | Need | ||||||
| A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| P0 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 2 |
| P1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| P2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| AVAILABLE | X=1, Y=2, Z=2 | ||||
With this availability, Process P1 can be served. Next state would become:
| Process | Max | Allocation | Need | ||||||
| A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| P0 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 2 |
| P1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| AVAILABLE | X=6, Y=4, Z=2 | ||||
With this availability, Process P2 can be served. Next state would become:
| Process | Max | Allocation | Need | ||||||
| A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| P0 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 4 | 2 |
| P1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AVAILABLE | X=8, Y=5, Z=3 | ||||
Finally, Process P0 will service:
| Process | Max | Allocation | Need | ||||||
| A | B | C | A | B | C | A | B | C | |
| P0 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P1 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| P2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| AVAILABLE | X=8, Y=5, Z=4 | ||||
So, Processes are in Safe state and Request 2 can be Permitted.
Program for Bankers algorithm in c with output
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
int Max[10][10], need[10][10], allocation[10][10], available[10], completed[10], safeSequence[10];
int p, r, i, j, process, count;
count = 0;
printf("Enter the number of processes : ");
scanf("%d", &p);
for(i = 0; i< p; i++)
completed[i] = 0;
printf("\nEnter the number of resources : ");
scanf("%d", &r);
printf("\nEnter the MAX Matrix for each process : \n");
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
printf("For process %d : ", i + 1);
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
scanf("%d", &Max[i][j]);
}
printf("\n\nEnter the ALLOCATION for each process : \n");
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
printf("For process %d : ",i + 1);
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
scanf("%d", &allocation[i][j]);
}
printf("\n\nEnter the AVAILABLE Resources : ");
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
scanf("%d", &available[i]);
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
need[i][j] = Max[i][j] - allocation[i][j];
do
{
printf("\n Max matrix:\tALLOCATION matrix:\n");
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
for( j = 0; j < r; j++)
printf("%d ", Max[i][j]);
printf("\t\t");
for( j = 0; j < r; j++)
printf("%d ", allocation[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
process = -1;
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
if(completed[i] == 0)
{
process = i ;
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
{
if(available[j] < need[i][j])
{
process = -1;
break;
}
}
}
if(process != -1)
break;
}
if(process != -1)
{
printf("\nProcess %d runs to completion!", process + 1);
safeSequence[count] = process + 1;
count++;
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
{
available[j] += allocation[process][j];
allocation[process][j] = 0;
Max[process][j] = 0;
completed[process] = 1;
}
}
}while(count != p && process != -1);
if(count == p)
{
printf("\nThe system is in a SAFE state!!\n");
printf("Safe Sequence : < ");
for( i = 0; i < p; i++)
printf("%d ", safeSequence[i]);
printf(">\n");
}
else
printf("\nThe system is in an UNSAFE state!!");
getch();
clrscr();
}
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
int Max[10][10], need[10][10], allocation[10][10], available[10], completed[10], safeSequence[10];
int p, r, i, j, process, count;
count = 0;
printf("Enter the number of processes : ");
scanf("%d", &p);
for(i = 0; i< p; i++)
completed[i] = 0;
printf("\nEnter the number of resources : ");
scanf("%d", &r);
printf("\nEnter the MAX Matrix for each process : \n");
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
printf("For process %d : ", i + 1);
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
scanf("%d", &Max[i][j]);
}
printf("\n\nEnter the ALLOCATION for each process : \n");
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
printf("For process %d : ",i + 1);
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
scanf("%d", &allocation[i][j]);
}
printf("\n\nEnter the AVAILABLE Resources : ");
for(i = 0; i < r; i++)
scanf("%d", &available[i]);
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
need[i][j] = Max[i][j] - allocation[i][j];
do
{
printf("\n Max matrix:\tALLOCATION matrix:\n");
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
for( j = 0; j < r; j++)
printf("%d ", Max[i][j]);
printf("\t\t");
for( j = 0; j < r; j++)
printf("%d ", allocation[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
process = -1;
for(i = 0; i < p; i++)
{
if(completed[i] == 0)
{
process = i ;
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
{
if(available[j] < need[i][j])
{
process = -1;
break;
}
}
}
if(process != -1)
break;
}
if(process != -1)
{
printf("\nProcess %d runs to completion!", process + 1);
safeSequence[count] = process + 1;
count++;
for(j = 0; j < r; j++)
{
available[j] += allocation[process][j];
allocation[process][j] = 0;
Max[process][j] = 0;
completed[process] = 1;
}
}
}while(count != p && process != -1);
if(count == p)
{
printf("\nThe system is in a SAFE state!!\n");
printf("Safe Sequence : < ");
for( i = 0; i < p; i++)
printf("%d ", safeSequence[i]);
printf(">\n");
}
else
printf("\nThe system is in an UNSAFE state!!");
getch();
clrscr();
}
Output:
Request 1: Additional process P0 requests for additional resources of 0 instances of A and 0 instances of B and 2 instances of C.
Request 2: Additional process P1 Requests for additional resources of 2 instances of A and 0 instances of B and 0 instances of C.


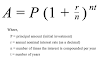
1 Comments
Nice...and thank you
ReplyDelete